What Is The Principle Of The Float Valve
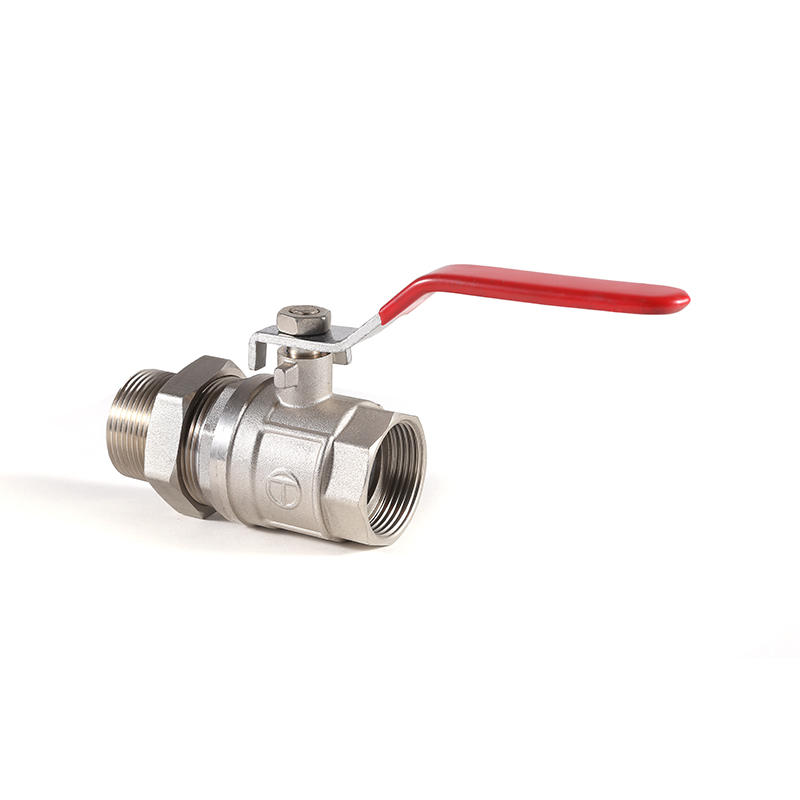
Float valve float: The core component of the float valve is a float, which is usually made of plastic or metal and is able to float in water.
Lever system: The float is connected to the valve through a lever system. When the water level rises, the float will also rise.
Valve control: As the float rises, it pushes the valve downward through the lever system, thereby closing the water inlet and preventing more water from entering the system.
Drop in water level: When the water level drops, the float also drops, pulling the valve upward through the lever system, opening the water inlet, and allowing water to flow back into the system. Clean.
Float Valve Maintenance and Selection
Float valves are essential components in various water systems, ensuring a constant and controlled water level. Their design, which includes a float, lever system, and valve control, makes them reliable and efficient. Understanding the details of float valve operation and maintenance can enhance their longevity and performance.
Materials and Durability
The float, typically made from plastic or metal, is designed to withstand prolonged exposure to water without degrading. Plastic floats are often preferred in applications where corrosion resistance is crucial, while metal floats, such as those made from stainless steel, are chosen for their strength and durability in more demanding environments.
In addition to the float, the lever system and valve components must also be robust. Materials such as brass or stainless steel are commonly used for these parts due to their strength and corrosion resistance. One such component that often pairs with float valves is the copper angle valve. Copper angle valves are valued for their durability and resistance to corrosion, making them a nice choice for controlling water flow in conjunction with float valves.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the smooth operation of float valves. Here are some tips for maintaining these components:
1. Inspection: Periodically inspect the float for any signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks or holes in plastic floats, and check metal floats for any signs of corrosion or dents.
2. Cleaning: Keep the float and valve components clean. Remove any debris or buildup that could interfere with the movement of the float or the operation of the valve.
3. Lubrication: Some lever systems may benefit from occasional lubrication to ensure smooth movement. Use a water-resistant lubricant appropriate for the materials involved.
4. Adjustment: Ensure that the float is correctly adjusted. An improperly adjusted float can incorrect water levels, causing the valve to open or close at inappropriate times. Refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for specific adjustment procedures.
Selection Considerations
Choosing the right float valve involves considering several factors:
1. Water System Requirements: Determine the water system's requirements, including the desired water level and the pressure at which the system operates. This will help in selecting a float valve with the appropriate specifications.
2. Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the float valve materials with the water being controlled. For instance, in systems with potable water, ensure that all materials are safe and compliant with relevant standards.
3. Connection Type: Ensure that the float valve's connection type matches the system's existing plumbing. Copper angle valves, for example, often have threaded connections that must match the system's pipe threads.
4. Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental conditions where the float valve will be used. For outdoor applications, ensure that the materials can withstand exposure to sunlight, temperature variations, and other environmental factors.
Applications
Float valves are versatile and find use in various applications:
1. Water Tanks: They are commonly used in water tanks to maintain a constant water level, ensuring that the tank does not overflow or run dry.
2. Cooling Systems: In industrial cooling systems, float valves help regulate the water level, ensuring efficient cooling performance.
3. Agricultural Irrigation: Float valves are used in irrigation systems to maintain consistent water levels in reservoirs, ensuring adequate water supply for crops.
4. Toilets and Cisterns: Household toilets often use float valves to control the water level in the cistern, ensuring proper flushing and refilling.
Float valves, with their simple yet effective design, are crucial for maintaining controlled water levels in various systems. Understanding the materials, maintenance practices, and selection criteria can help ensure their reliable performance. By choosing the right float valve and accompanying components like copper angle valves, and maintaining them properly, you can enhance the efficiency and longevity of your water systems.
-
Feedback


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Email us now!
Email us now!